Psychiatric Outcomes in Patients with Trigeminal Neuralgia Treated with Anticonvulsants and Antidepressants: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using a National Database
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5195/ijms.2025.2726Keywords:
Trigeminal Neuralgia, Chronic Pain, Depression, Anxiety, Sleep DisordersAbstract
Background: Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) is a chronic craniofacial condition characterized by intense, sporadic shocks of pain through the trigeminal nerve. The unpredictable and severe nature of these episodes can be physically and mentally debilitating, significantly affecting the quality of life and often leading to anxiety, depression, and sleep disorders. This study investigated the psychiatric outcomes of anxiety, depression, and sleep disorders in TN patients who were treated with both anticonvulsants and antidepressants, compared to those who were treated only with anticonvulsants, to explore a multi-modal approach for addressing both pain and psychiatric symptoms.
Methods: A retrospective analysis of electronic health records was conducted using TriNetX, a collaborative health network encompassing over 250 million patient records worldwide. The analysis included 15,129 patient records, comparing two cohorts of TN patients.
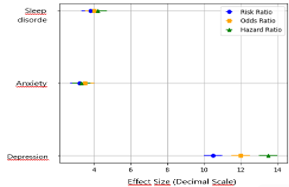
Results: After adjusting for demographic factors, both cohorts were predominately female (73%), white (70%), and about 59 years of age. The results indicated that patients taking both anticonvulsants and antidepressants had higher risk, odds, and hazard ratios for developing depression (RR 10.448, OR 10.906, HR 10.763), anxiety (RR 2.680, OR 3.210, HR 3.013), and sleep disorders (RR 3.595, OR 3.696, HR 3.697) compared to those taking only anticonvulsants.
Conclusion: Despite limitations including inability to assess dosage and severity of pain, these findings suggest that concurrent use of anticonvulsants and antidepressants may exacerbate psychiatric symptoms in TN patients. However, these effects might improve with appropriate dosage adjustments, highlighting the need for including dosage adjustments and monitoring.
References
National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR). Craniofacial pain conditions. NIDCR. Available from: https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/research/data-statistics/craniofacial-pain-conditions. Accessed 2024 Jun 28.
Cruccu G, Gronseth G, Alksne J, Argoff C, Brainin M, Burchiel K, et al. AAN-EFNS guidelines on trigeminal neuralgia management. Eur J Neurol. 2008;15(10):1013–28.
Cruccu G, Gronseth G, Alksne J, Argoff C, Brainin M, Burchiel K, et al. Trigeminal neuralgia: new classification and diagnostic grading for practice and research. Neurology. 2016;87(2):220–8.
Miki K, Mori K, Hagiwara S, Tachibana M, Chiba K, Maeda M. Trigeminal neuralgia caused by a persistent primitive trigeminal artery variant and superior cerebellar artery. NMC Case Rep J. 2019;6(4):101–3.
Wu TH, Hu LY, Lu T, Chen PM, Chen HJ, Shen CC, et al. Risk of psychiatric disorders following trigeminal neuralgia: a nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study. J Headache Pain. 2015;16:64.
Tampi RR, Tampi DJ, Balachandran S, et al. Antipsychotics, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, melatonin, and benzodiazepines for behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: a systematic review of meta-analyses. Curr Treat Options Psych. 2017;4(1):55–79.
Vigo DV, Baldessarini RJ. Anticonvulsants in the treatment of major depressive disorder: an overview. Harv Rev Psychiatry. 2009;17(4):231–41.
Prabhavalkar KS, Poovanpallil NB, Bhatt LK. Management of bipolar depression with lamotrigine: an antiepileptic mood stabilizer. Front Pharmacol. 2015;6.
Araya EI, Claudino RF, Piovesan EJ, Chichorro JG. Trigeminal neuralgia: basic and clinical aspects. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2020;18(2):109–19.
Ware K, Tillery E, Linder L. General pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic concepts of mood stabilizers in the treatment of bipolar disorder. Ment Health Clin. 2016;6(1):54–61.
Lawthom C, Didelot A, Coppola A, Aledo-Serrano Á, Fazekas B, Sainz-Fuertes R, et al. The impact of epilepsy and antiseizure medications on sleep: findings from a large European survey in adults with epilepsy and matched controls. Epilepsy Behav. 2023;148:109000.
Luo Y, Zhang Y, Hu X, Zhang L, Wang J, Hu D, et al. A research on quality of life score (QOLS) of patients with trigeminal neuralgia (TN). J Infect Public Health. 2019;12(5):690–4.
Franzen PL, Buysse DJ. Sleep disturbances and depression: risk relationships for subsequent depression and therapeutic implications. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2008;10(4):473–81.
Steiger A, Pawlowski M. Depression and sleep. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):607.
Huff T, Weisbrod LJ, Daly DT. Neuroanatomy, cranial nerve 5 (trigeminal). In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482283/.
Yang S, Chang MC. Chronic pain: structural and functional changes in brain structures and associated negative affective states. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(13):3130.
Surah A, Baranidharan G, Morley S. Chronic pain and depression. Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain. 2014;14(2):85–9.
Di Stefano G, Truini A, Cruccu G. Real-world effectiveness and tolerability of carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine in 354 patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Eur J Pain. 2021;25(6):1229–35.
Punyawudho B, Cloyd JC, Leppik IE, Ramsay RE, Marino SE, Pennell PB, et al. Characterization of the time course of carbamazepine deinduction by an enzyme turnover model. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009;48(5):313–9.
Afonso AS, Carnaval T, Cés SV. Combination therapy for neuropathic pain: a review of recent evidence. J Clin Med. 2021;10(16):3533.
Sohi G, Lao N, Caraceni A, et al. Nonopioid drug combinations for cancer pain: a systematic review. Pain Rep. 2022;7(2):e995.
Kaeley N, Kabi A, Bhatia R, Mohanty A. Carbamazepine-induced hyponatremia: a wakeup call. J Fam Med Prim Care. 2019;8(5):1786–8.
Lien YHH. Antidepressants and hyponatremia. Am J Med. 2018;131(1):7–8.
Bojdani E, Souza FD, Rajagopalan A, et al. Hyponatremia and psychiatric diseases. Weight Manag.
Sawant NS, Parkar SR, Rupani K, et al. Hyponatremia misdiagnosed as depression. Ann Indian Psychiatry. 2019;3(2):168.
Grunze A, Amann BL, Grunze H. Efficacy of carbamazepine and its derivatives in the treatment of bipolar disorder. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(5):433.
Simon LV, Keenaghan M. Serotonin syndrome. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482377/.
Volpi-Abadie J, Kaye AM, Kaye AD. Serotonin syndrome. Ochsner J. 2013;13(4):533–40.
Rybakowski JK. Mood stabilizers of first and second generation. Brain Sci. 2023;13(5):741.
Pain O, Hodgson K, Trubetskoy V, Ripke S, Marshe VS, Adams MJ, et al. Identifying the common genetic basis of antidepressant response. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2021;2(2):115–26.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ashley Deng, Priya Kaneria , Eduardo Espiridion

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- The Author retains copyright in the Work, where the term “Work” shall include all digital objects that may result in subsequent electronic publication or distribution.
- Upon acceptance of the Work, the author shall grant to the Publisher the right of first publication of the Work.
- The Author shall grant to the Publisher and its agents the nonexclusive perpetual right and license to publish, archive, and make accessible the Work in whole or in part in all forms of media now or hereafter known under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License or its equivalent, which, for the avoidance of doubt, allows others to copy, distribute, and transmit the Work under the following conditions:
- Attribution—other users must attribute the Work in the manner specified by the author as indicated on the journal Web site; with the understanding that the above condition can be waived with permission from the Author and that where the Work or any of its elements is in the public domain under applicable law, that status is in no way affected by the license.
- The Author is able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the nonexclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the Work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), as long as there is provided in the document an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post online a prepublication manuscript (but not the Publisher’s final formatted PDF version of the Work) in institutional repositories or on their Websites prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work. Any such posting made before acceptance and publication of the Work shall be updated upon publication to include a reference to the Publisher-assigned DOI (Digital Object Identifier) and a link to the online abstract for the final published Work in the Journal.
- Upon Publisher’s request, the Author agrees to furnish promptly to Publisher, at the Author’s own expense, written evidence of the permissions, licenses, and consents for use of third-party material included within the Work, except as determined by Publisher to be covered by the principles of Fair Use.
- The Author represents and warrants that:
- the Work is the Author’s original work;
- the Author has not transferred, and will not transfer, exclusive rights in the Work to any third party;
- the Work is not pending review or under consideration by another publisher;
- the Work has not previously been published;
- the Work contains no misrepresentation or infringement of the Work or property of other authors or third parties; and
- the Work contains no libel, invasion of privacy, or other unlawful matter.
- The Author agrees to indemnify and hold Publisher harmless from the Author’s breach of the representations and warranties contained in Paragraph 6 above, as well as any claim or proceeding relating to Publisher’s use and publication of any content contained in the Work, including third-party content.
Enforcement of copyright
The IJMS takes the protection of copyright very seriously.
If the IJMS discovers that you have used its copyright materials in contravention of the license above, the IJMS may bring legal proceedings against you seeking reparation and an injunction to stop you using those materials. You could also be ordered to pay legal costs.
If you become aware of any use of the IJMS' copyright materials that contravenes or may contravene the license above, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org
Infringing material
If you become aware of any material on the website that you believe infringes your or any other person's copyright, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org







