A Cross Sectional Study on Adherence to Medication among Patients with Hypertension and/or Diabetes Attending One of the Tertiary Care Institutes of Ahmedabad City, Gujarat, India
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5195/ijms.2025.2598Keywords:
Morisky Medication Adherence, Hypertension, DiabetesAbstract
Background: The lifelong management of chronic diseases such as Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus necessitates a comprehensive approach, including lifestyle modifications and consistent adherence to medication. Present study aimed to evaluate treatment adherence among patients with diabetes and /or hypertension attending a tertiary care institute in Ahmedabad city, India.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among 200 patients aged over 18 years, diagnosed with diabetes and/or hypertension. The sample population was selected from a tertiary care institute at Ahmedabad city using a consecutive sampling method. Data collection utilized a pretested and predesigned proforma along with the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8).
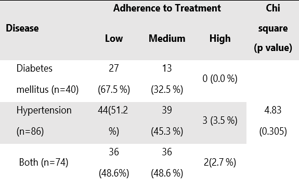
Results: Hypertension was present in 43.0% of the participants, while 20.0% reported diabetes mellitus. Additionally, 37.0% had both conditions. Out of total 200 patients 53.5% exhibited low adherence to treatment. Lower adherence to treatment was found to be more among Diabetics (67.5%) as compared to hypertensive patients (51.2%). Among participants having comorbidities 48.6% had low adherence to treatment. The association between disease type and adherence levels was not significant (p-value = 0.305). Not having any symptoms and forgetfulness were common reasons for low adherence among 41.1% and 24.2% of participants, respectively.
Conclusion: This study highlights the need for targeted interventions aimed at enhancing medication adherence among individuals managing with chronic illnesses like hypertension and diabetes. The findings provide valuable insights for healthcare professionals and policymakers to develop effective strategies for improving treatment adherence and subsequently mitigating the progression of these chronic conditions.
References
Joshi SR, Parikh RM. India – Diabetes capital of the world: Now heading towards hypertension. J Assoc Physicians India. 2007;55:323–4.
World Health Organization (WHO). What is adherence. WHO.2003. pages 17–18. Available from: https://www.who.int/chp/knowledge/publications/adherence_Section1.pdf. Cited on May 29, 2023
Bhandari S, Sarma PS, Thankappan KR. Adherence to antihypertensive treatment and its determinants among urban slum dwellers in Kolkata, India. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2015;27(2):74-84.
Venkatachalam J, Abrahm SB, Singh Z, Stalin P, Sathya GR. Determinants of Patient's Adherence to Hypertension Medications in a Rural Population of Kancheepuram District in Tamil Nadu, South India. Indian J Community Med. 2015 40(1):33-7.
Mishra R, Sharma SK, Verma R, Kangra P, Dahiya P, Kumari P, Sahu P, Bhakar P, Kumawat R, Kaur R, Kaur R, Kant R. Medication adherence and quality of life among type-2 diabetes mellitus patients in India. World J Diabetes. 2021 15;12(10):1740-1749.
Venkatesan M, Dongre AR, Ganapathy K. A Community-Based Study on Diabetes Medication Nonadherence and its Risk Factors in Rural Tamil Nadu. Indian J Community Med. 2018;43(2):72-76.
Lavakumar S, Jesurun RS. A study on the level of drug compliance among the outpatients who are on a long-term drug therapy in a tertiary care teaching hospital at Kancheepuram district in Tamil Nadu. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 2017;10:174-6.
Rao CR, Kamath VG, Shetty A, Kamath A. Treatment Compliance among Patients with Hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Coastal Population of Southern India. Int J Prev Med. 2014;5(8):992-8.
Pentapati SSK, Debnath DJ. Updated BG Prasad's classification for the year 2022. J Family Med Prim Care. 2023;12(1):189-190.
Morisky DE, Ang A, Krousel-Wood M, Ward HJ. Predictive validity of a medication adherence measure in an outpatient setting. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2008;10(5):348-54.
Surekha A, Fathima FN, Agrawal T, Misquith D. Psychometric properties of Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS) in known diabetic and hypertensive patients in a rural population of Kolar District, Karnataka. Indian J Public Heal Res Dev. 2016;7:250–256.
Balasubramanian A, Nair SS, Rakesh PS, Leelamoni K. Adherence to treatment among hypertensives of rural Kerala, India. J Family Med Prim Care. 2018;7(1):64-69.
Rao CR, Kamath VG, Shetty A, Kamath A. Treatment Compliance among Patients with Hypertension and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Coastal Population of Southern India. Int J Prev Med. 2014;5(8):992-8.
Pokharel P, Jha SK, Adhikari A, Katwal S, Ghimire S, Shrestha AB, Poudel N. Non-adherence to anti-hypertensive medications in a low-resource country Nepal: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 19;85(9):4520-4530.
Sahoo J, Mohanty S, Kundu A, Epari V. Medication Adherence Among Patients of Type II Diabetes Mellitus and Its Associated Risk Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital of Eastern India. Cureus. 2022 29;14(12):e33074.
Sweileh WM, Aker O, Hamooz S. Rate of compliance among patients with diabetes mellitus and hypertension. An-Najah Univ J Research-A-(Natural Sciences) 2005;19:1–12.
Published
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Janak Patel, Kanal Shah, Jayveer Jain, Venu Shah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- The Author retains copyright in the Work, where the term “Work” shall include all digital objects that may result in subsequent electronic publication or distribution.
- Upon acceptance of the Work, the author shall grant to the Publisher the right of first publication of the Work.
- The Author shall grant to the Publisher and its agents the nonexclusive perpetual right and license to publish, archive, and make accessible the Work in whole or in part in all forms of media now or hereafter known under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License or its equivalent, which, for the avoidance of doubt, allows others to copy, distribute, and transmit the Work under the following conditions:
- Attribution—other users must attribute the Work in the manner specified by the author as indicated on the journal Web site; with the understanding that the above condition can be waived with permission from the Author and that where the Work or any of its elements is in the public domain under applicable law, that status is in no way affected by the license.
- The Author is able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the nonexclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the Work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), as long as there is provided in the document an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post online a prepublication manuscript (but not the Publisher’s final formatted PDF version of the Work) in institutional repositories or on their Websites prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work. Any such posting made before acceptance and publication of the Work shall be updated upon publication to include a reference to the Publisher-assigned DOI (Digital Object Identifier) and a link to the online abstract for the final published Work in the Journal.
- Upon Publisher’s request, the Author agrees to furnish promptly to Publisher, at the Author’s own expense, written evidence of the permissions, licenses, and consents for use of third-party material included within the Work, except as determined by Publisher to be covered by the principles of Fair Use.
- The Author represents and warrants that:
- the Work is the Author’s original work;
- the Author has not transferred, and will not transfer, exclusive rights in the Work to any third party;
- the Work is not pending review or under consideration by another publisher;
- the Work has not previously been published;
- the Work contains no misrepresentation or infringement of the Work or property of other authors or third parties; and
- the Work contains no libel, invasion of privacy, or other unlawful matter.
- The Author agrees to indemnify and hold Publisher harmless from the Author’s breach of the representations and warranties contained in Paragraph 6 above, as well as any claim or proceeding relating to Publisher’s use and publication of any content contained in the Work, including third-party content.
Enforcement of copyright
The IJMS takes the protection of copyright very seriously.
If the IJMS discovers that you have used its copyright materials in contravention of the license above, the IJMS may bring legal proceedings against you seeking reparation and an injunction to stop you using those materials. You could also be ordered to pay legal costs.
If you become aware of any use of the IJMS' copyright materials that contravenes or may contravene the license above, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org
Infringing material
If you become aware of any material on the website that you believe infringes your or any other person's copyright, please report this by email to contact@ijms.org







